Rice planting technology (I)
Time:2023-01-31 Follow:981

Rice is divided into indica rice and japonica rice, early rice and mid-late rice, glutinous rice and non-glutinous rice according to the type of rice. It can be divided into conventional rice and hybrid rice according to the way of planting. There are other classifications, which can be divided into paddy rice and floating rice according to soilless cultivation or not; According to the life cycle, it can be divided into seasonal rice and "lazy rice" (over-year ratooning rice); According to height, it can be divided into ordinary rice and giant rice of about 2 meters; According to salt and alkali tolerance, it can be divided into ordinary freshwater rice and "sea water rice".

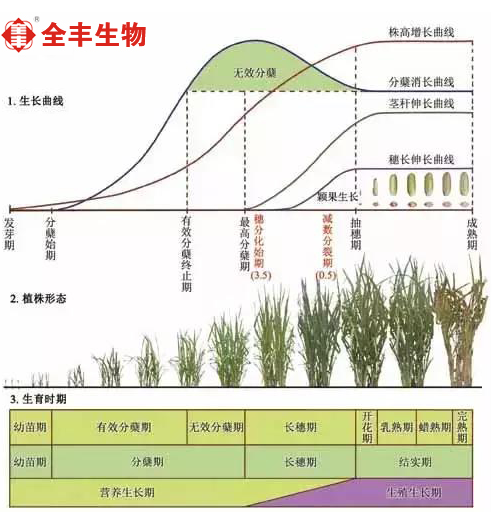
In rice, seeds are usually germinated to produce new seeds, which is a growth cycle of rice, that is, the growth period. The growth period can be divided into seedling stage, turning green stage, tillering stage, long spike stage (spike differentiation stage) and seed setting stage.
Seedling stage: including germination, germination and trefoil stage.
Greening period: the buffer period for rice survival from seedling field to Honda after transplanting.
Tillering stage: including initial stage, peak stage, final stage (high tillering stage) and effective tillering termination stage which determines the key period of spike number.
Long ear stage: including ear differentiation stage, jointing stage and booting stage when the sheath of flag leaf bulges.
Seed setting stage: including heading and flowering stage, milk maturity stage, wax maturity stage, yellow maturity stage and full maturity stage.
In order to do a good job in rice seedling breeding, we should select good varieties, do a good job in selecting and drying seeds, soaking seeds with chemicals, and accelerating germination with proper temperature, strengthen the management of seedling fields, and adopt the "four control and one prevention" technical measures to control the sowing date, the sowing amount, the water, the length, and the disease and insect pests, so as to achieve a complete seedling.
1. Seed treatment
Before planting, select excellent rice seeds, and select well-adapted pure and full seeds according to local weather changes and soil conditions. Then soak the seeds and disinfect them. When disinfecting, pay attention not to damage the seeds. Disinfectants such as strong chlorine essence can be used, which can effectively disinfect the seeds without causing damage. After soaking the seeds, take them out and wrap them with wet gauze to accelerate germination. Control the temperature at about 31 degrees. Pay attention to the pile turning when the temperature increases. When most of the seeds are exposed, reduce the temperature to about 25 degrees. During germination, pay attention to the temperature change, control the temperature within the appropriate range, and timely sow and raise seedlings after the germination is done in the shade and air.

2. Seedling raising and transplanting
The common method of raising rice seedlings in China's rural areas is to raise seedlings in the seedling tray, prepare the nutrient soil in the seedling tray, and apply sufficient base fertilizer. The base fertilizer is mainly farmyard fertilizer, and mix it with the soil evenly with appropriate amount of compound fertilizer. When the temperature is above 7 ℃, timely sow, cover with fine soil after sowing, improve the soil temperature, and ensure that the seeds can germinate normally and all kinds of nutrients required for germination. Seedling management should be done well after emergence. High-quality rice seedlings are the key to ensure successful rice planting. When the seedlings grow to about 8 cm, they can be transplanted.

3. Water and fertilizer management
It is very necessary to manage the water content of rice. It is necessary to ensure that shallow water is used frequently at the tillering stage, sufficient water is used to dry the field at the seedling stage, shallow water is used frequently at the young spike differentiation stage, the water layer is maintained at the heading and flowering stage, and dry and wet alternate at the milking stage.
It is very important to drain and sun the field after the rice tillering stage and before the young spike differentiation. It can reasonably control the ineffective tillers, further improve the lodging resistance ability, at the same time enhance the absorption of nutrients by rice, effectively improve the growth status of rice roots, and more conducive to the root down, thus improving the yield of rice.
Fertilization of rice is also very important. The tillering stage of rice is the first stage in which rice needs a large amount of fertilizer, so the first topdressing should be carried out. Adequate nutrition can promote the growth of rice seedlings, ensure the fullness of rice quality, and improve the yield. In the middle and later stages, fertilizer can be applied appropriately according to the soil and rice growth.

In the process of cultivation, the amount of fertilizer applied to rice should be reasonably controlled. The fertilizer should be used in stages and batches, with the former heavy and the latter light, and the latter should pay attention to the supplement of phosphorus and potassium fertilizer. In addition, silicon and zinc have a great impact on the yield and quality of rice.
Base fertilizer: mainly organic fertilizer, supplemented by quick-acting fertilizer. Generally, 2000~3000 kg of organic fertilizer+7~8 kg of urea, 30~40 kg of superphosphate, 8~10 kg of potassium chloride or 30~40 kg of balanced compound fertilizer are applied per mu.
Tillering fertilizer: it can be applied as early as possible after transplanting and turning green to promote the growth of low-node tillers, and play the role of ear enhancement, which can be carried out twice. After turning green for the first time, apply 7~8 kg of urea or high-nitrogen compound fertilizer per mu, and appropriate amount of calcium sulfate and zinc sulfate to promote tillering; For the second time, 7~8 kg of urea or high-nitrogen compound fertilizer per mu was applied at the peak tillering stage to ensure the orderly growth of the whole field and to protect the tillering and ear formation.
Ear fertilizer: after the rice is sunned, the ear fertilizer should be applied in time to promote the development of young ears. The application of ear fertilizer should be carried out from the time of closing to the time of jointing. It is better to apply the ear fertilizer when the young ear differentiation is 1 to 2 stages. About 20 kg of potassium chloride+8 to 10 kg of urea should be used per mu.
Granular fertilizer: 5~7 days before the break, if the leaf spike is too green, it will be harmful to the later filling and the maintenance of green leaves. At this time, 3~5 kg of urea per mu will be applied to avoid premature leaf senescence after the break heading.
Foliar topdressing: rice can be mixed with foliar fertilizer to topdressing outside the root during the jointing to filling period, in combination with disease and pest control drugs. The fertilizer can be selected from phosphorus and potassium source and sink, urea, silicon fertilizer, boron fertilizer, etc., and applied in the critical period of fertilizer demand such as break, booting and heading.

The picture is from the network. If it is the same, please contact to delete it




